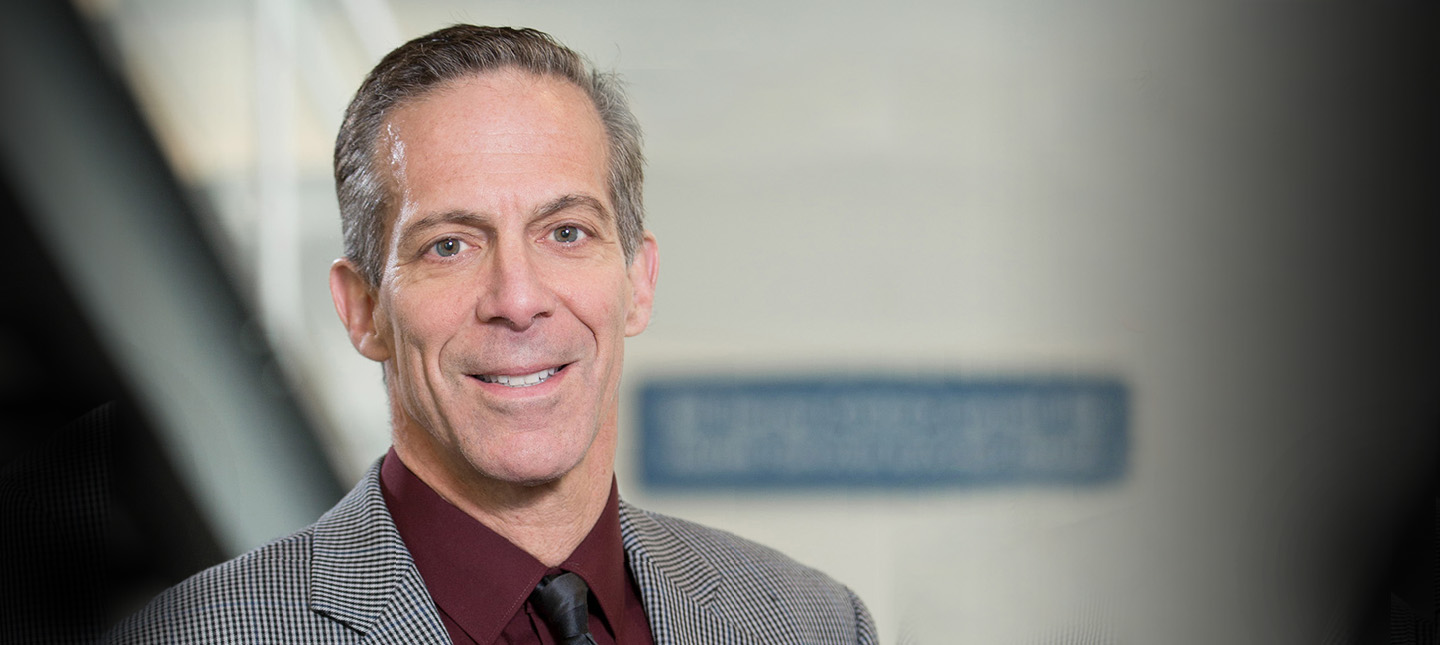
Admission to the hospital and being seen by a neurologist are factors associated with better quality care for people with a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as mini-stroke, according to new research led by scientists from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute, Purdue University, and Indiana University. The study looked at patients treated in the U.S. Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
“There has been a movement to avoid hospital admission for patients with TIAs and instead create observation units to allow patients to get care quickly and be sent home,” said Dawn Bravata, M.D., senior author of the paper and a research scientist at the VA and Regenstrief. “However, this study supports the idea that admission may still lead to improved care.” Dr. Bravata is also a professor at Indiana University School of Medicine.
Patients with TIA are at high risk of more vascular events, including repeated TIAs, stroke and death. Timely care has been shown to substantially reduce those risks. However, because TIAs are considered less serious than strokes and there is often uncertainty about diagnosis, patients with TIA are less likely to be admitted to the hospital for treatment than patients with stroke.
The researchers undertook this study to understand both the patient and facility factors that influence care quality, which includes characteristics such as a patient’s health history, date and time of the visit to the emergency department, and staffing at the VA facility.
The research team, which also included scientists from Yale School of Medicine and Michigan State University, analyzed data from 3,052 VHA patients with a TIA treated between October 2010 and September 2011. They looked at four indicators to measure care quality: brain imaging, carotid artery imaging, statin therapy and antithrombotic therapy. Then they developed a multilevel, structural equation model that allowed them to evaluate the complex relationship between both patient and facility characteristics and the association with composite quality of care measure.
Findings showed:
- Care quality was most strongly affected by admission to the hospital,
- Patients who received a neurological consultation had overall higher care quality,
- Speech impairment was associated with higher hospital admittance,
- Weekend arrivals lowered the likelihood of neurological consultation but increased the likelihood of inpatient admission,
- Fewer neurologists on staff was associated with fewer consultations and admissions,
- And a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (higher burden of comorbid diseases such as cancer or heart disease) was associated with higher hospital admittance but lower neurological consultation.
“The patients who are admitted to the hospital have the highest quality of care, and are more likely to have a neurological consultation, which is also a strong driver of care quality,” said Dr. Bravata. “The next steps are to determine the best approach to ensuring that all TIA patients get access to the necessary neurological treatment, regardless of the facility where they receive care. The VA recently instituted a teleneurology program to expand access to neurology across facilities, but it is too soon to tell its effect on care.”
Study authors say an alternative to hospital admission could be comprehensive follow-up TIA care in the outpatient setting, however, these care models have not been widely adopted in the U.S.
“Modelling care quality for patients after a transient ischaemic attack within the US Veterans Health Administration” was published in BMJ Open Quality. The project was supported by funding from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research and Development Service, Stroke Quality Enhancement Research Initiative Service Directed Project (SDP 12-178). Support for VA/Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Service (CMS) data is provided by the Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Services Research and Development Service, VA Information Resource Center (SDR 02-237 and 98-004).
Greg Arling, PhD from the Purdue University School of Nursing and the VA Health Services Research and Development (HSR&D) Precision Monitoring to Transform Care (PRIS-M) Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI), Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center is the first author on the paper.
Other authors are Jason J. Sico, M.D. from Yale School of Medicine and Clinical Epidemiology Research Center, VA Connecticut Health System West Haven Campus; Matthew J. Reeves, PhD from VA HSR&D PRIS-M QUERI, Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center and Michigan State University; Laura Myers, PhD from the VA HSR&D PRIS-M QUERI and Center for Health Information and Communication, Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center; and Fitsum Baye, M.S., from VA HSR&D PRIS-M QUERI, Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center and Indiana University School of Medicine.
About Regenstrief Institute
Founded in 1969 in Indianapolis, the Regenstrief Institute is a local, national and global leader dedicated to a world where better information empowers people to end disease and realize true health. A key research partner to Indiana University, Regenstrief and its researchers are responsible for a growing number of major healthcare innovations and studies. Examples range from the development of global health information technology standards that enable the use and interoperability of electronic health records to improving patient-physician communications, to creating models of care that inform practice and improve the lives of patients around the globe.
Regenstrief Institute is celebrating 50 years of healthcare innovation. Sam Regenstrief, a successful entrepreneur from Connersville, Indiana, founded the institute with the goal of making healthcare more efficient and accessible for everyone. His vision continues to guide the institute’s research mission.
More about Dawn Bravata, M.D.
In addition to her role as a research scientist at Regenstrief, Dawn M. Bravata, M.D., is a professor of clinical medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine. She also serves as a core investigator for the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs Health Services Research and Development Center for Health Information and Communication at Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical Center and is a co-principal investigator for VA HRS&D PRIS-M QUERI.