Commentary in npj Digital Medicine says improving patient matching is critical and doable
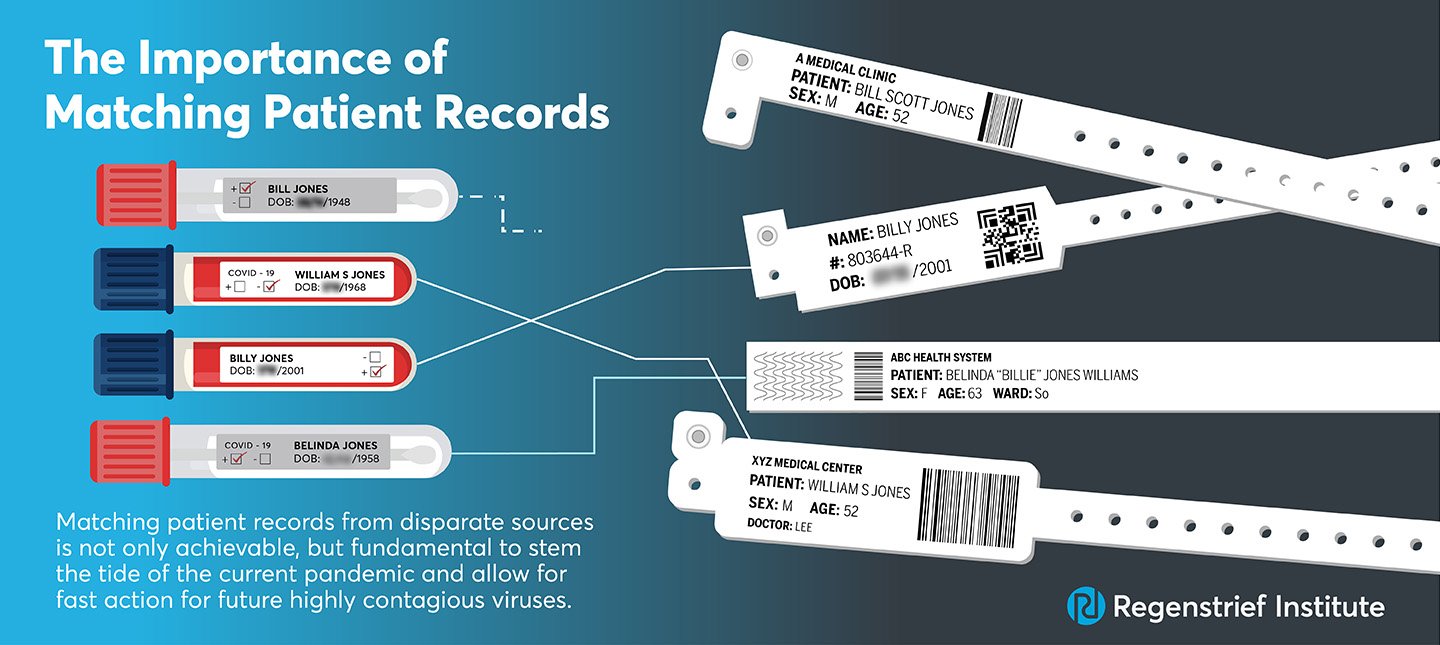
In a peer-reviewed commentary published in npj Digital Medicine, experts from Regenstrief Institute, Mayo Clinic and The Pew Charitable Trusts write that matching patient records from disparate sources is not only achievable, but fundamental to stem the tide of the current pandemic and allow for fast action for future highly contagious viruses.
Specifically, rapid identification of COVID-19 infected and at-risk individuals and the success of future large-scale vaccination efforts in the United States will depend, in part, on how effectively an individual’s electronic health data is securely shared among healthcare providers, care settings including hospitals and pharmacies, and other systems used to track the illness and immunization.
For data sharing to be effective, electronic health records (EHRs) — both those held within a single facility and those in different healthcare organizations — must correctly refer to a specific individual. Is Billy Jones known at a different doctor’s office as William Jones and are all his health records linked? To which Maria Garcia do lab test results belong? Which John Smith was referred to during contact tracing?
Unfortunately, the commentary notes, patient matching rates vary widely, with healthcare facilities failing to link records for the same patient as often as half the time. Authors Shaun Grannis, M.D., vice president for data and analytics at Regenstrief Institute and Regenstrief Professor of Medical Informatics at Indiana University School of Medicine; John D. Halamka, M.D., president of Mayo Clinic Platform and Ben Moscovitch, director of The Pew Charitable Trusts’ health information technology initiative, call for stakeholders to urgently address the patient matching conundrum. Otherwise, the commentary says, efforts to curtail the current pandemic and future ones will be ill-advisedly delayed.
“…the sharing of more data and use of standards — reflect near-term opportunities that government and health care organizations can implement to respond to the current pandemic and prepare for future ones. In the longer term, there may be other opportunities — such as use of biometrics, unique identifiers, or multi-factor authentication — that could further enhance patient identification and matching, including for routine care. However, those options — and the associated standards that underlie their success — while worthwhile to examine, cannot be designed, deployed, and implemented in a near-term manner that could help mitigate the effects of this pandemic,” the commentary states.