A large study has found that commencing treatment for sleep apnea as soon as possible after a stroke or a mini-stroke significantly improves speech impairment and other neurological symptoms as well as walking and other physical functioning.
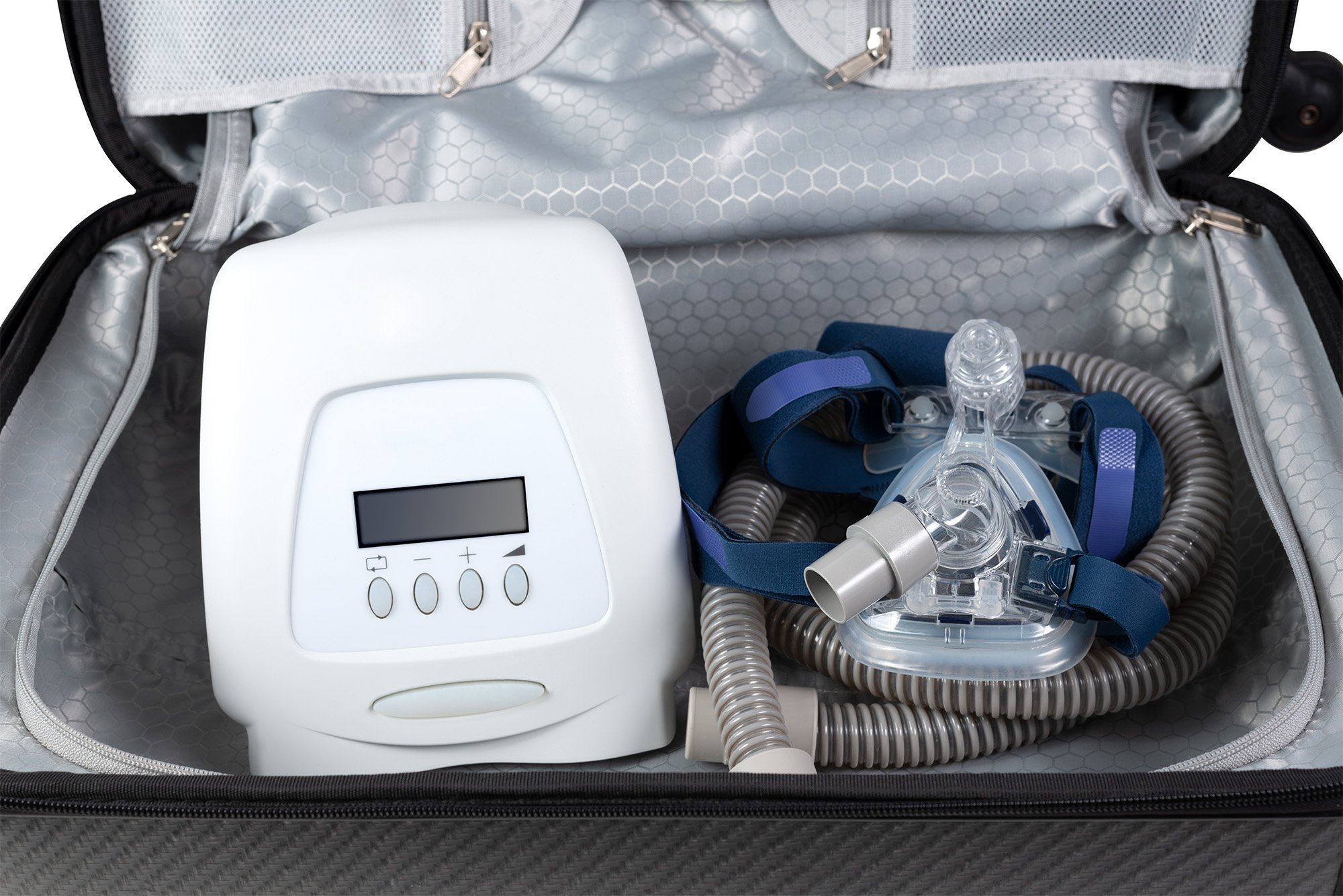
“We have shown, for the first time in a randomized controlled study, that for individuals who have had a stroke or a TIA — a Transient Ischemic Attack, also known as a mini-stroke — the diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea with CPAP [Continuous Positive Airway Pressure] therapy provides significant benefits, even greater than the benefits of tPA [tissue plasminogen activator], the FDA-approved drug treatment for stroke,” said Regenstrief Institute and Roudebush VA Medical Center research scientist Dawn Bravata, M.D., who led the study.
“That’s a substantial clinical effect. The added good news for stroke patients is that CPAP has been used as a sleep apnea therapy for many years, and it has an excellent safety record,” she said.
“Diagnosing and Treating Sleep Apnea in Patients with Acute Cerebrovascular Disease” is published online ahead of print in the Journal of The American Heart Association.
Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, more than 780,000 strokes occur annually in the U.S.
TIAs produce symptoms similar to those of a stroke, but typically last only a few minutes and usually cause no permanent damage. An estimated one-quarter of individuals who experience a TIA will eventually have a stroke, with about half of these strokes occurring within 12 months after the mini-stroke.
Sleep apnea is common among patients with stroke or TIA. Although few stroke patients are currently diagnosed and treated, approximately two out of three are thought to have sleep apnea, a disorder in which breathing during sleep is irregular. Sleep apnea may cause low oxygen levels, high blood pressure, and heart rhythm issues.
CPAP for sleep apnea can be used safely in addition to other stroke therapies, most of which have known adverse effects. For example, tPA, a clot buster, can induce non-trivial bleeding.
The new study followed individuals who had strokes or TIAs for up to one year after the event. Two-thirds of the 252 study participants, 41 percent of whom were female and 36 percent of whom were black, were able to use CPAP effectively.
“Preliminary data suggests the sooner you treat sleep apnea in stroke patients with CPAP, the more potent the effect of that treatment,” said Dr. Bravata. “Usually diagnosing sleep apnea is an outpatient service, but we need to make sleep testing acutely available to stroke and TIA patients in the hospital as part of their work-up, just as we do brain imaging, lab testing and cardiac monitoring as part of the initial stroke/TIA evaluation.
“This will require changes in sleep medicine services by healthcare systems as they care for stroke patients; but the benefits of acute sleep apnea management are now clear,” Dr. Bravata said.
Patients in the study were from five hospitals in two states. They were randomized to a control group (usual care) without sleep apnea treatment or to one of two intervention groups (standard or enhanced care), both of which included sleep apnea diagnosis and treatment.
National stroke guidelines recommend testing for sleep apnea, however, past observational studies have shown that it is not being done. Dr. Bravata believes that with the results of large studies like this one, diagnosing and treating sleep apnea post-stroke acutely will become a routine part of standard practice.
In addition to her appointment as a Regenstrief Institute investigator, Dr. Bravata is a faculty member of Indiana University School of Medicine. The study team also included Regenstrief Institute investigators Edward J. Miech, Ed.D.; Marianne S. Matthias, Ph.D.; and Linda S. Williams, M.D. and researchers from IU School of Medicine, Yale School of Medicine, VA Connecticut Healthcare System and New York University. The study was supported by a grant (U34 HL105285-01) from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.